In today’s data-driven economy, speed and simplicity are amongst the most important things. From data access to application responsiveness, performance matters more than ever. Whether your users are accessing files from shared storage or your applications are writing data to a database, how fast data is read, written, and accessed determines how good or bad the user experience will be. Given the increasing reliance on data accessibility from different locations and access methods, it is important for IT teams to ensure a highly available and performant infrastructure that delivers an enhanced data experience for users.
While user experience is focused on the user-facing applications and the front-end interactivity, data experience goes much deeper. Data experience spans the entire data path from user access to applications all way to the backend storage infrastructure. The experience your data gets reflects on the experience your user gets.
This blog will focus on understanding how to deliver an enhanced data experience so that your users enjoy faster, easier, and anytime access to data. Let’s dive right in.
#1 Ensure the Right Data is at the Right Place at the Right Time
One key aspect of delivering the best data experience is ensuring data gets treated properly when it comes to storing it. You may have a mix of highly performant premium storage devices, low-performance commodity storage, and also S3 cloud storage. It is important to implement machine learning techniques to automatically track data patterns (access temperature, type/size/age of files, whether it is a replica or original data, etc.) and place data accordingly on the appropriate storage.
- From a performance standpoint, you don’t want to have cold data on your performant SAN/NAS device. Freeing them up from infrequently accessed data will result in improved storage performance and, in turn, application responsiveness and data experience.
- From a cost standpoint, you don’t want to fill up your on-premises storage with snapshots taken for backup or redundant data. Cloud/object storage may be a better fit for this.
There are changes happening to data all the time. What is considered hot data today can become archived tomorrow; what was inactive for a long time can be accessed again, updated, and become active. Manually keeping track of data access patterns is extremely tedious and close to impossible. A software-defined storage solution can help automate data placement to meet your needs so that you don’t have to manually figure out which data goes where and when.

#2 Optimize Capacity and Balance Load to Ensure High Storage Efficiency
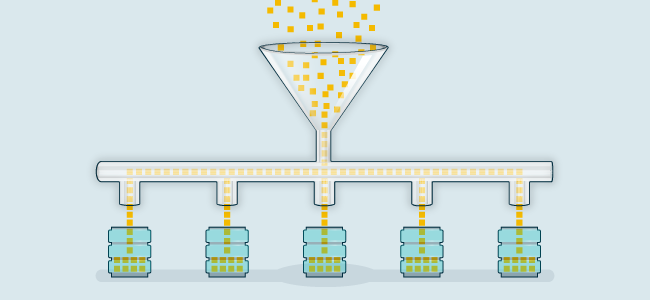
As we observed above, an overstressed storage device may not yield the best efficiency. IT teams need to optimize capacity through storage best practices such as:
- Aggregating capacity from disparate storage devices under a storage pool to reclaim all unused space and balancing load across them.
- Thin-provisioning storage to overcommit capacity to applications initially and then dynamically allocating actual disk space when needed.
- Using data reduction techniques (deduplication and compression), which help optimize capacity by removing duplicate datasets and compressing data to reduce the storage space required.
Balancing load, capacity, and throughput (in a parallel processing storage architecture) can help avoid performance bottlenecks and lead to a seamless data experience.
#3 Implement Data Redundancy and Protection Schemes for Continuous Access
Data availability is the first step to accessing the data. IT/storage administration teams must implement proper business continuity (BC) and disaster recovery (DR) strategies to address outages and other unexpected storage failures.
- Creating data redundancies through synchronous mirroring and setting up an automatic failover mechanism will help achieve zero-RPO and zero-RTO recovery without any data loss.
- DR/cloud sites can also be used to store redundant data copies. Asynchronous replication can be leveraged to create copies and send over to the DR site. In the event of a failure of the primary site, the DR/cloud site can restore connectivity with very minimal data loss.
- Data protection schemes using a combination of erasure coding and replication are also common in storage environments where increasing data durability is key.
- Having simultaneous access by many users/apps to the same dataset can slow down accessibility. Creating distributed copies of data locally and spreading access requests over these redundant copies can help improve read IOPS and consequently data experience for users.
These techniques help increase data availability, ensuring continuous access and business operations.

#4 Intelligent Management of Unstructured Data
Especially in the unstructured data universe (file and object storage), users accessing data face unique challenges. Because most environments are distributed by design and files are scattered over different devices and sites, there is always the challenge of searching to find files from different namespaces specific to each file or object store. Collaboration and file sharing between users from different locations is key issue that needs to be addressed.
A software-defined approach to data management involves creating a single global file system that assimilates all other namespaces across existing diverse storage media under it. So, an end user looking for a file needs to just search in one place to retrieve it. When the existing folder structure is retained, it becomes even more easy for navigating to, accessing, and sharing the file. This saves considerable time and effort for users who are otherwise just bouncing between namespaces to search for files.
On the object storage side, where data is being archived for long-term preservation and content delivery, IT teams must look for ways to:
- Enable end users to store, organize, find and share files
- Support distributed collaboration and content delivery
- Customize/add metadata to enrich the value of data
- Share or stream content directly from the archive
- Edit specific portions of a file (e.g., a video file) directly from the archive
All these empower the administrator to store and manage data with ease, while enhancing the data experience for the end user.

#5 Flexible Access Methods for Broader Accessibility
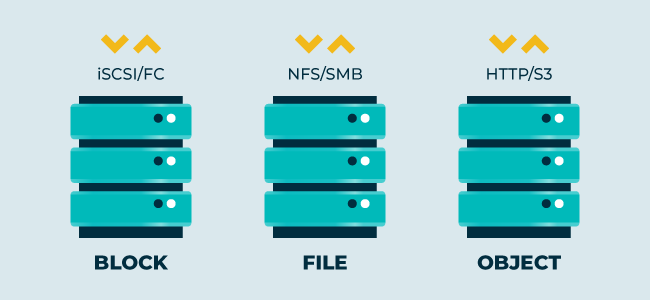
Applications and users need to have convenient access to data wherever they are connecting from. Based on the class of storage (block, file, or object) you are having in your IT environment, your storage infrastructure needs to support the most commonly used protocols:
- For data on block storage: Fibre Channel, iSCSI
- For data on file storage: NFS, SMB
- For data on object/cloud storage: S3, HTTP
Flexibility in supporting data access is critical to support different use cases.
Better business outcomes begin with a great data experience. IT teams have an instrumental role to enable business success for their organization. Consider implementing software-defined storage solutions to increase data availability, simplify data access and collaboration, and strengthen data protection. Contact DataCore to learn more about our software-defined solutions for block, file, and object storage and how they can elevate the data experience for your organization.